Recent News
-

Algorithms for a fairer world
CategoriesMachine learning technologies hold the potential to revolutionize decision-making. But how can we ensure AI systems are free of bias? Our experts weigh in.
-

Seeking smarter surgery
CategoriesJohns Hopkins researchers are using Loop-X Mobile Imaging Robot by Brainlab to forge the future of the intelligent operating room.
-

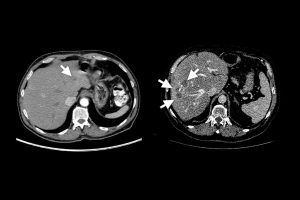
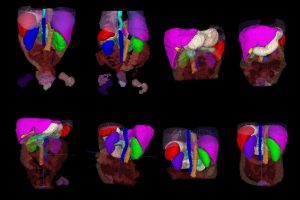
The Hopkins-led team demonstrated that an AI model trained solely on synthetic tumor data works as well as models trained on real tumors.
-

The importance of ambiguity
CategoriesJohns Hopkins researchers find that large language models can handle multiple interpretations of the same sentence—but only if they’re told to.
-

Smartphone videos are often the first to capture news events. Johns Hopkins researchers are developing a tool to make that footage more searchable and contextualized.
-

Johns Hopkins researchers investigate how machine learning classifiers can be made more resistant to adversarial attacks on their input.